GIS-based Forest Fire Susceptibility Analysis Using Frequency Ratio, Statistical Index and Weighting Factor Techniques
Thai Journal of Science and Technology (TJST) Vol.10, No.6
Worawit Suppawimut*, Baromasak Klanreungsang and Ratchaphon Samphutthanont
Published: Apr 20, 2023
https://li01.tci-thaijo.org/index.php/tjst/article/view/253362
Abstract
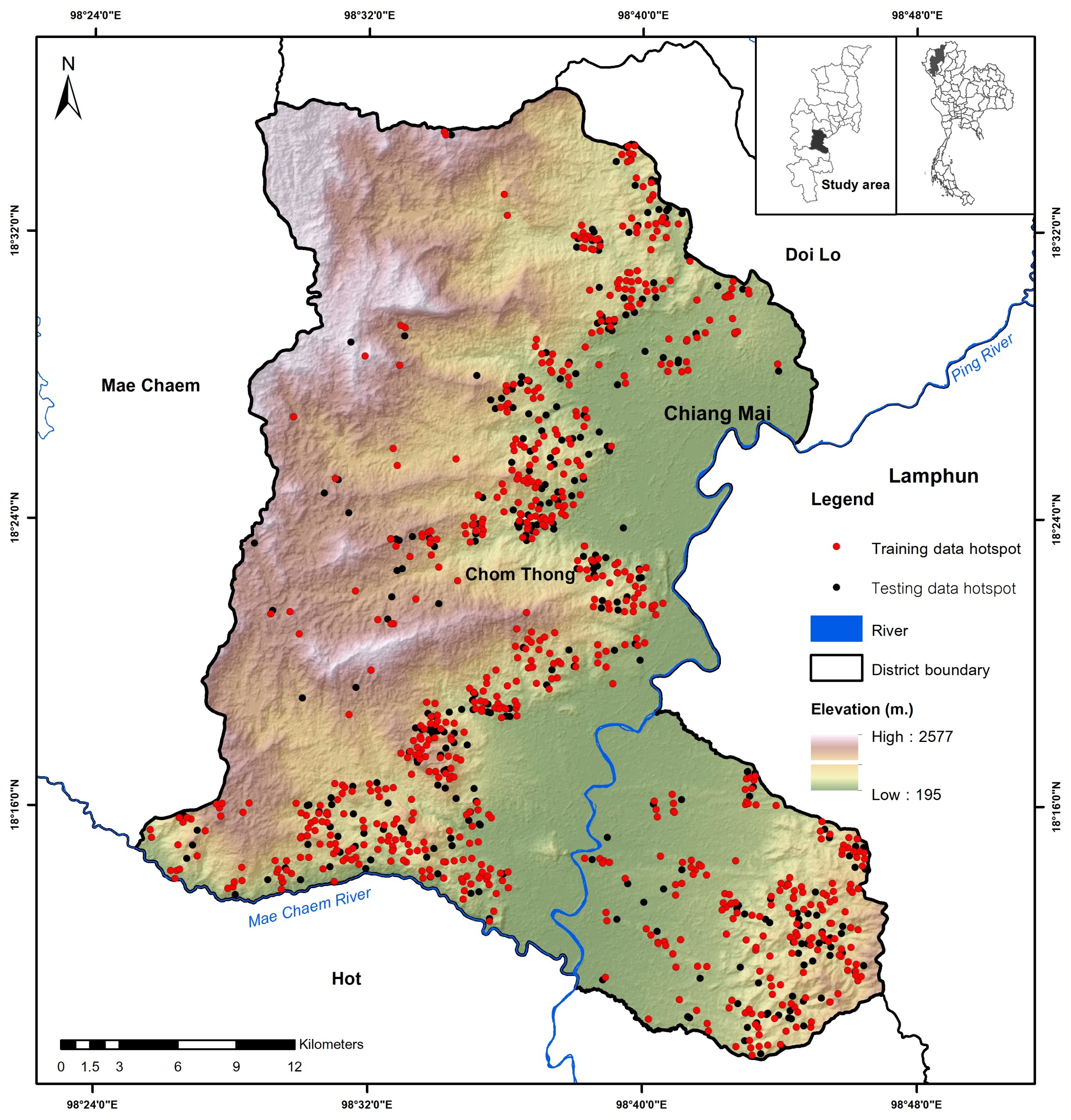
The objective of this study was to apply a geographic information system for analyzing forest fire susceptibility area in Chom Thong District, Chiang Mai Province using frequency ratio (FR), statistical index (SI), and weighting factor (WF) techniques. The hotspot location data of 745 and 306 points were used as training and testing data. This study used 8 conditioning factors for the analysis namely elevation, slope, aspect, topographic wetness index (TWI), normalized vegetation index (NDVI), rainfall, stream density, and land use. All conditioning factors and the training data were analyzed for the rating and weighting scores. The forest fire susceptibility area was classified as five susceptible levels including very high, high, moderate, low, and very low susceptible levels. The result of FR, SI, and WF, revealed that 12.88, 20.39, and 21.34 percent of the total area were identified as the very high susceptible area for forest fire where were mostly found in the central of the study area. The WF result revealed that the three most influencing factors were elevation, rainfall, and land use. Lastly, the validation results using the AUC value show that the success rates were 83.73, 80.90, and 70.50 for WF, SI, and FR methods respectively while the prediction rates of WI, SI, and FR were 84.41, 80.77, and 70.62 respectively.