Bayesian Network Integration with GIS for the Analysis of Areas Vulnerable to the Outbreak of COVID-19 in Bangkok, Thailand
International Journal of Geoinformatics Volume 18, No. 5
B. Klanreungsang
Geography and Geoinformatics, Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, Chiang Mai RajabhatUniversity, Thailand
W. Suppawimut
Geography and Geoinformatics, Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences, Chiang Mai RajabhatUniversity, Thailand
Published: Oct 27, 2022
DOI: https://doi.org/10.52939/ijg.v18i5.2373
Abstract
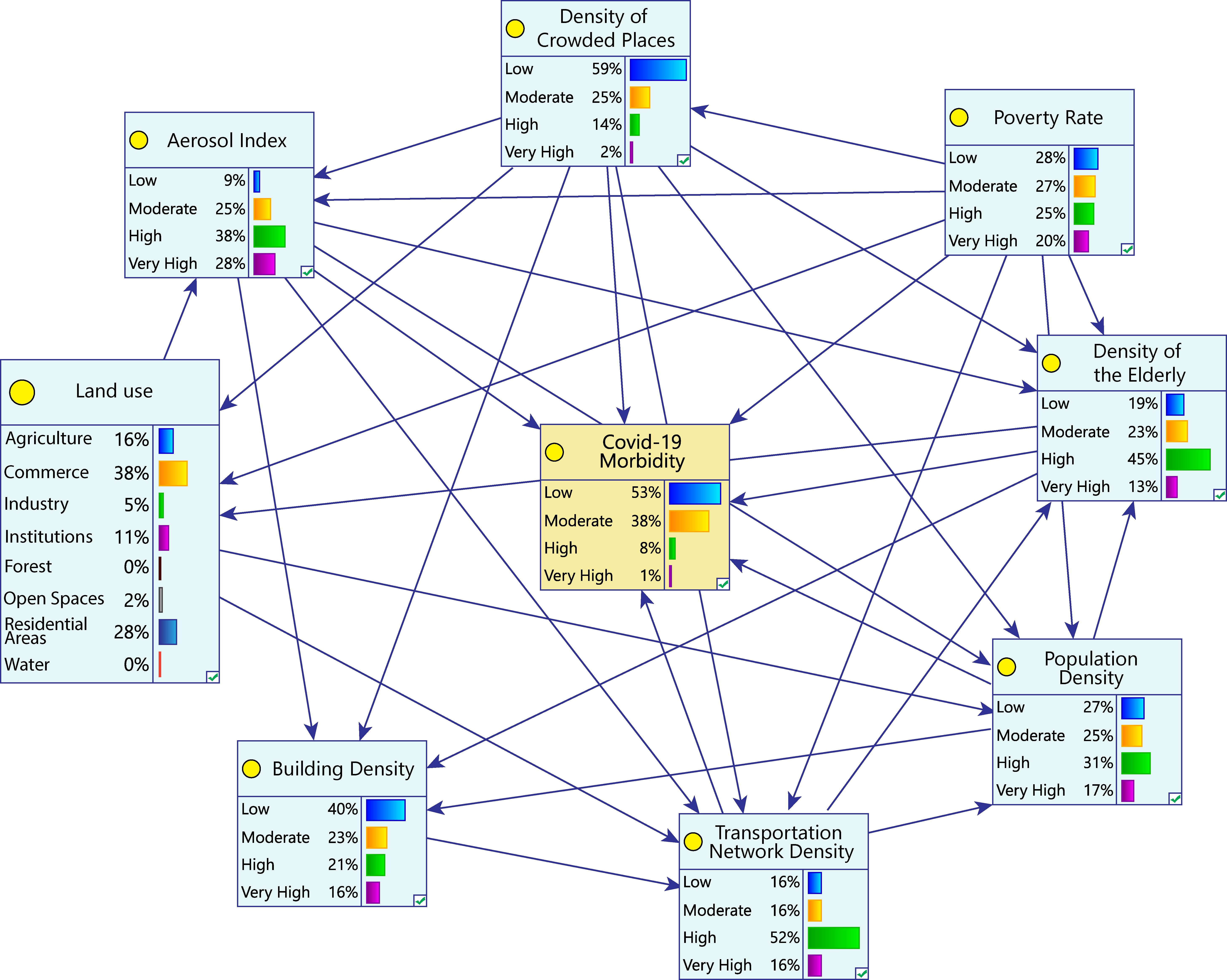
The COVID-19 pandemic prompted a search for a new method of preventing the spread of this virus. This study established a model of the areas in Bangkok which were vulnerable to the COVID-19 pandemic by using a combination of the Bayesian network (BN) and the geographic information system (GIS). The model was developed using a data-driven approach and was evaluated with 10-fold cross validation and ROC analysis. The results demonstrated that the proposed method effectively predicted the vulnerability of disease outbreak. The most vulnerable areas to the pandemic were around the center and in the west of Bangkok, while the areas of low vulnerability were found in the north and east of the city. Population density and the aerosol index were highly influential factors in the outbreaks, affirmed by sensitivity analysis. Furthermore, the model used to conduct a scenario analysis resulted in the identification of vulnerability management strategies.